Understanding the hydrological valley landscape: A multi-scenario adaptive framework for delineating valley floors
May 7, 2025·,,,,,,·
0 min read
Wenjie Sun
Yang Chen
Xingyu Zhou
Xin Yang
Junfei Ma
Sijin Li
Guoan Tang
Abstract
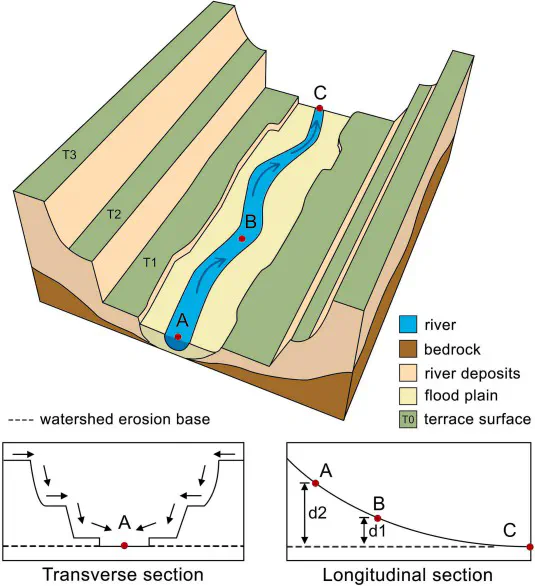
As critical zones in fluvial geomorphology shaped by hydrological processes, valley floors play an essential role in material exchange and circulation between upland and groundwater bodies. Accurate delineation of valley floors is crucial for understanding river morphology, analyzing the spatial distribution of valley floor sediments, and maintaining the riverine ecosystem. However, existing delineation methods often rely heavily on manual interpretation, are limited in regional applicability, and require subjective parameter selection. This underscores the need for a method that incorporates adaptive thresholding and ensures broad applicability across diverse regions. In response to this challenge, we develop a multi-scenario adaptive framework for delineating valley floors. This framework designs several indicators for detecting topographical cross-sectional and longitudinal features, which enables the accurate and automated extraction of valley floor boundaries through adaptive thresholding. The framework includes the following components:(1) The initial drainage network was extracted by setting drainage thresholds based on geomorphological texture features obtained using the gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM); (2) The drainage network generated in the previous step was filtered by calculating the average river gradient and setting adaptive parameters, removing drainage networks located in steep valleys; (3) The valley floor extent was adaptively extracted by proposing terrain factors such as slope accumulation and its variation. The experimental results demonstrate that this method applies to the extraction of valley floors in various landscape types, exhibiting remarkable precision. This study also explored the correlation between valley floor, geological sedimentation, and surface hydrological processes, finding a significant consistency between sediment distribution and valley floor extent. These findings offer valuable perspectives on valley floor evolution, river restoration, and sustainable water resource management.
Type
Publication
CATENA